SecPod Community › Forums › Security Intelligence › Alert! Zerologon: Your Windows Domain Controller Can’t Handle Zero Properly
Tagged: Security Intelligence
- This topic has 0 replies, 1 voice, and was last updated by
Community Manager.
-
AuthorPosts
-
-
May 30, 2025 at 11:01 am #6473
Microsoft team patched a critical and exciting vulnerability in the Netlogon Remote Protocol of the Windows server last month. zero logon vulnerability discovered by the Cybersecurity firm Secura (dubbed as Zerologon), has received the highest severity score of 10.0. The vulnerability is identified as CVE-2020-1472 and allows an attacker to successfully compromise the vulnerable Domain controller by just setting up a TCP connection with it. This vulnerability is treated as severe because even an unauthenticated attacker can gain the Domain Admin privileges by using the domain controller credentials. A vulnerability management tool can stop the same.
Microsoft team patched a critical and exciting vulnerability in the Netlogon Remote Protocol of the Windows server last month. zero logon vulnerability discovered by the Cybersecurity firm Secura (dubbed as Zerologon), has received the highest severity score of 10.0. The vulnerability is identified as CVE-2020-1472 and allows an attacker to successfully compromise the vulnerable Domain controller by just setting up a TCP connection with it. This vulnerability is treated as severe because even an unauthenticated attacker can gain the Domain Admin privileges by using the domain controller credentials. A vulnerability management tool can stop the same.
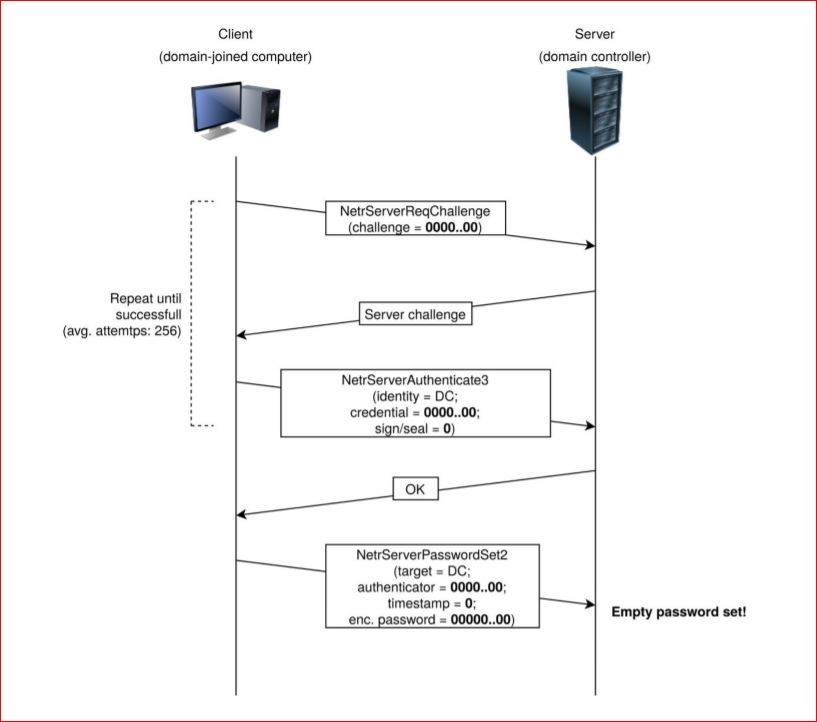
Netlogon AES-CFB8 cryptographic negotiation algorithm flaw:
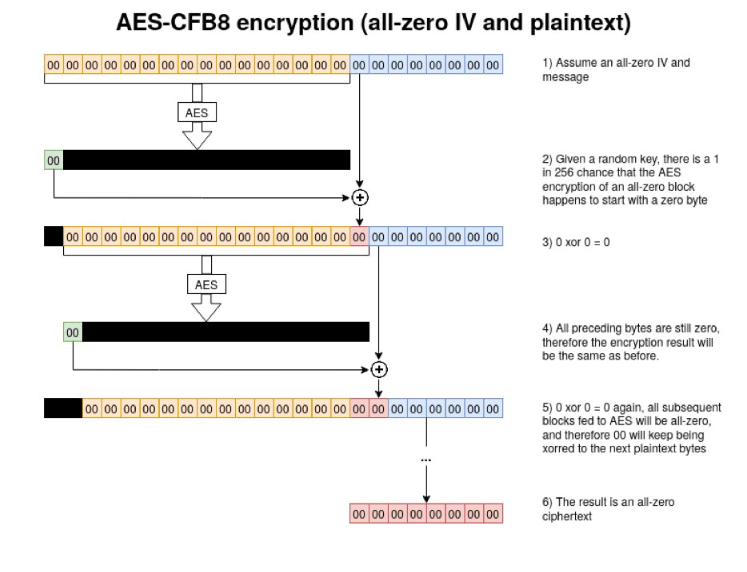
When encrypting a message consisting only of zeroes, with an all-zero Initialisation Vector(IV), there is a 1 in 256 chance that the output will also contain only zeroes.
Proof-of-Concept in zero logon vulnerability:
A PoC is published to exploit this vulnerability. As you can see below, this is the part of the exploit function in POC. Here the flaw in the AES-CFB8 algorithm is know the Client Credential. When the plaintext and ciphertext set to 8 zeros, for 1 in 256 session keys, the correct Client Credential will consist of 8 zeroes.plaintext = b’\x00′ * 8
ciphertext = b’\x00′ * 8try:
server_auth = nrpc.hNetrServerAuthenticate3(
rpc_con, dc_handle + ‘\x00’, target_computer + ‘$\x00’, nrpc.NETLOGON_SECURE_CHANNEL_TYPE.ServerSecureChannel,
target_computer + ‘\x00’, ciphertext, flags
)
assert server_auth[‘ErrorCode’] == 0Here when assert server_auth[‘ErrorCode’] value becomes zero, we assume our plaintext value is the right one and hence the client credential can be obtained. Further, the attacker can make use of NetrServerPasswordSet2 function to update the password to the desired value. Similarly, any computer in the domain can compromise including admin.
Impact of zero logon vulnerability
An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability can take over the domain controller. Run a specially crafted application on any device on the network.Affected Products
Affects all Microsoft Windows Servers that use MS-NRPC to connect to a domain controller except server 2008.Microsoft Windows Server 2019
Microsoft Windows Server 2016
Microsoft Windows Server 2012
Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 Service Pack 1Solution
Microsoft has released a security fix in its monthly Patch Tuesday updates for August 2020.SanerNow security content has published to detect and mitigate these vulnerabilities. We strongly recommend applying the security updates as soon as possible following the instructions published in our support article.
-
-
AuthorPosts
- You must be logged in to reply to this topic.
